
With the progress in integrated circuit technology, the digital IC’s are becoming smaller and faster and as a result the transfer rates in Parallel Communication with multiple lanes have reached a bottle neck.
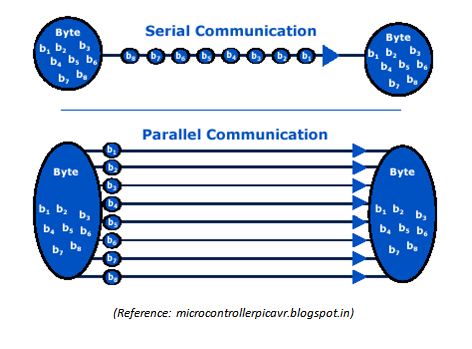
Olden day’s printers are the best example for external parallel communication. Parallel Data Transfer methods are faster and expensive as they needs more hardware and a lot of wires. This is possible because parallel data transfer uses multiple lanes or wires between the transmitter and receiver in order to transfer the data. In parallel data transfer, all the bits are transferred from the source to destination at once. Transfer of Digital Data from one device to another can be achieved in two ways: Parallel Data Transfer and Serial Data Transfer.
UART is one of the most simple and most commonly used Serial Communication techniques. This is contrast to SPI or I2C, which are just communication protocols. The hardware for UART can be a circuit integrated on the microcontroller or a dedicated IC.

UART or Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter is a dedicated hardware associated with serial communication.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
